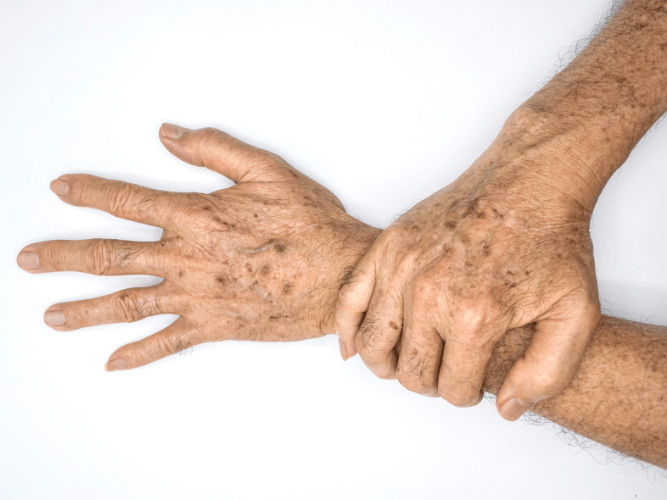
Age spots, also called sunspots or liver spots, are flat, dark patches that develop on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. They are caused by overactive pigment cells and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. While harmless, they can resemble skin cancer and may be removed for cosmetic reasons. Treatments include topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, and cryotherapy. Prevention involves daily sunscreen use, wearing protective clothing, and minimizing sun exposure during peak hours.
What Are Age Spots?
Age spots are small, flat, tan to dark brown patches that appear on skin frequently exposed to the sun. They are a common sign of sun damage and skin aging, often appearing after the age of 40 but can also develop in younger individuals with excessive sun exposure. Unlike freckles, age spots do not fade over time without treatment and tend to darken with further UV exposure.
Symptoms of Age Spots
- Flat, oval areas of increased pigmentation: These spots often have well-defined borders and a uniform color. unlike other skin conditions like freckles..
- Tan to dark brown in color: The color intensity depends on sun exposure and skin type.
- Commonly appear on the face, hands, shoulders, arms, and upper back .
- Vary in size from small freckles to half an inch in diameter: Some spots may enlarge or cluster together over time.
- May cluster together, forming larger pigmented areas: Multiple age spots can merge, creating larger patches of discoloration.
- Hormonal changes – Some research suggests that fluctuations in hormones can contribute to pigmentation changes: Pregnancy, menopause, or hormone therapy may influence melanin production.
Causes of Age Spots
Age spots form due to overactive melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) stimulated by UV radiation. Other contributing factors include:
- Prolonged sun exposure without protection: UV rays accelerate melanin production, leading to pigmentation changes over time.
- Frequent use of tanning beds: Artificial UV exposure has similar effects to natural sunlight, increasing the risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics – family history increases the risk: If close relatives have age spots, you may be more likely to develop them.
- Skin aging – natural melanin production changes : As the skin ages, melanin distribution becomes uneven, causing dark spots to appear.
- Hormonal changes – fluctuations in hormones can contribute to pigmentation changes: Pregnancy, menopause, or hormone therapy may influence melanin production.
Who Is at Risk for Age Spots?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing age spots:
- Individuals over 40 years old: Aging skin is more susceptible to pigmentation irregularities.
- People with fair skin: Lighter skin has less melanin, making it more vulnerable to UV damage.
- Those with frequent sun exposure or history of sunburns: Repeated sun damage leads to cumulative pigmentation changes.
- Regular users of tanning beds: Artificial UV exposure can have long-term effects similar to excessive sun exposure.
- Individuals with a history of sunburns during childhood: Childhood sunburns increase the risk of developing age spots later in life.
- People who spend a lot of time outdoors without adequate sun protection: Outdoor activities without sunscreen can accelerate sun damage.
Diagnosis of Age Spots
Dermatologists diagnose age spots through a visual examination, checking the color, size, and shape of the affected areas. Most age spots have well-defined edges and uniform pigmentation, distinguishing them from other skin conditions. If a spot appears irregular, has multiple colors, or changes in size, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out skin cancer and ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Age Spots
Age spots are harmless but can be treated for cosmetic reasons. Treatment options include:
1. Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone Creams – Lightens dark spots by reducing melanin production: This ingredient is commonly used to fade hyperpigmentation over time.
- Retinoids (Tretinoin) – Promotes skin cell turnover to fade discoloration: Retinoids speed up skin renewal, helping new, even-toned skin to appear.
- Vitamin C Serums – Antioxidant that helps brighten skin tone and reduce pigmentation: Vitamin C neutralizes free radicals and reduces melanin synthesis.
- Kojic Acid & Glycolic Acid – Common ingredients in over-the-counter fade creams that help exfoliate the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation: These acids remove dead skin cells and promote brighter skin.
- Niacinamide – A form of vitamin B3 that helps to brighten skin and reduce pigmentation: Niacinamide regulates melanin production and improves overall skin texture.
2. Medical Procedures
- Laser Therapy – Targets melanin deposits for spot removal: Laser treatments break down melanin, allowing the body to eliminate dark spots naturally.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) – Uses light waves to break up pigment: IPL penetrates deep into the skin to target excess pigmentation while improving overall skin tone.
- Cryotherapy (Freezing) – Liquid nitrogen destroys pigment-producing cells: This method freezes dark spots, causing them to peel off over time.
- Chemical Peels – Removes top skin layers, allowing new, evenly pigmented skin to regenerate: Peels containing glycolic or trichloroacetic acid help fade discoloration by accelerating skin renewal.
- Microdermabrasion & Dermabrasion – Exfoliates and renews skin texture: These techniques mechanically exfoliate the skin, improving pigmentation irregularities over time.
How to Do Microdermabrasion & Dermabrasion at Home.
Instead of booking expensive appointments, you can remove age spots at home with microdermabrasion, saving both time and money. This non-invasive exfoliation technique gently removes the outer layer of skin, helping to fade dark spots, improve texture, and boost collagen production. Using a manual diamond or crystal-infused surface, at-home microdermabrasion promotes skin renewal, making age spots less noticeable over time. With just a few minutes per week, you can achieve professional-quality results without the hassle of clinic visits. For best outcomes, follow with moisturizer and daily sunscreen to protect your newly refreshed skin.

Try Microdermabrasion at home..
Prevention of Age Spots
To minimize age spots and prevent new ones:
- Use Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen (SPF 30+) daily, even on cloudy days: UV exposure occurs even on overcast days, making daily sun protection essential.
- Wear Protective Clothing like hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves: Clothing with UV protection can shield your skin from harmful rays.
- Limit Sun Exposure between 10 AM and 4 PM, when UV rays are strongest: Midday sun exposure is the most damaging, so seek shade during peak hours.
- Avoid Tanning Beds, which accelerate pigmentation changes: Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation that can lead to premature skin aging and dark spots.
- Use Antioxidant-Rich Skincare – Ingredients like vitamin C and E help combat free radicals caused by sun exposure: These antioxidants help neutralize oxidative damage that contributes to age spots.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet – Foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins can promote healthier skin: Eating fruits and vegetables high in vitamins A, C, and E can support skin health and prevent hyperpigmentation.
When to See a Doctor
Age spots are typically benign, but consult a dermatologist if a spot:
- Grows rapidly or changes shape: Rapid growth could indicate an abnormal skin condition.
- Has irregular borders or multiple colors: Uneven borders and mixed pigmentation may require medical evaluation.
- Appears black or starts bleeding: These changes could signal more serious conditions like melanoma.
- Becomes itchy or irritated: Persistent irritation should be assessed by a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Age spots are harmless but common signs of sun damage. While they don’t pose health risks, they can be treated for cosmetic concerns using topical treatments, laser therapy, and chemical peels. Prevention is key, and daily sunscreen use and sun protection can help reduce their occurrence. Maintaining a proper skincare routine and a healthy lifestylecan also help keep your skin even-toned and youthful. If any skin spots change in appearance, it’s best to consult a dermatologist for evaluation.